Electrical Motors are the backbone of Industry processes. The motors can be affected by different types of issues and finally this scenario can crash industry.
Motors can face a lot of faults like:
- Bearing failure
- Bearing failure
- Locked rotor
- Overheating
- Overloads (electrical and mechanical)
- Phase imbalance and any voltage imbalance will lead to an even higher current unbalance
- Running in reverse
- Shaft misalignment
- Vibration
Some of the above listed faults are Electrical and some are Mechanical faults. These faults can burn the motor and damage it severely if not protected properly. There are different types of tests performed to check the machine’s condition. The tests are classified into:
- Static Motor Testing
- Dynamic Motor Testing
These tests are carried out to check the motor’s condition in static and running condition when the supply is on or off respectively.
Static Motor Testing
This testing is also called offline testing. These tests are performed when the power supply is not provided to the machine.
This type of testing is used to check machine’s insulation. Machine insulation comprises two types of categories: copper to copper insulation and copper to ground insulation.
To perform the insulation testing thoroughly following tests are carried out:
- Winding resistance Test
- Meg-ohm Test
- Polarization index Test
- Step-voltage or high potential Test
- Surge Test
Combination of the above listed tests will assess the integrity of the entire insulation system.
Necessity of Tests
Most short-circuits in power systems occur because of insulation failure. It can occur in case of overstressing and degradation of insulation with the passage of time. It can also happen due to sudden overvoltage condition.
Effects of Insulation failure upon Motor
- It will cause Motor shaft voltage that tries to force current into the shaft bearing, leading to early bearing failure.
- It will produce Motor stray capacitance (between windings and earthed frame) that will lead to earth-current flow caused by high dV/dt.
- It will create high dV/dt that creates non-uniform distribution of voltage across the winding, with high voltage drop across the first few turns and consequential failures.
- In a large motor, voltage differential on the frame is likely to develop in spite of protective earthing of the motor. More than one earthing point is needed.

Dynamic Motor Testing
Dynamic Motor Testing is also called on-line testing as motor is checked when electric supply is provided to the machine. In dynamic tests, Motor’s data such as voltage, current, torque, load, efficiency etc is collected to indicate the machine’s condition.
This type of testing generates information about Power Quality, Motor’s Mechanical issues and Load. This testing equipment is also capable to not only to calculate torque value but also spectrum of torque to see torque ripples.
Power quality information is very favorable as it will give insight about voltage level, voltage unbalances, harmonic distortion, current levels and current unbalances.
Dynamic testing is also of much interest as it is also used to see rotor bar issue.
Rotor Bar Faults
Rotor is the most stressed part of the machine. In this article, we will try to emphasize upon some types of causes of rotor and rotor bar failures. Moreover, we will also discuss how to identify these faults of rotors.
Causes of Rotor Failures:
Rotors during machine’s operation always face different types of stresses called thermal, magnetic, dynamic, environmental, mechanical and residual stresses. The rotors remain in healthy condition till the stresses are under allowable levels. But whenever these stresses cross these limits, rotors got failure and life of motor is greatly reduced.

Thermal Stresses:
These stresses appear during starting, running or stalled conditions. When motor is in stalled condition, there will appear a large potential and can damage the rotor in a very short time.
This type of stress can be detected by using current sensing devices which can monitor and measure heavy current and trip the power supply.
There are also other causes of thermal stresses such as:
- Excessive no. of motor starts
- Rotor stalling
- Insufficient airflow
- Bearing failure
- Unbalanced phase voltage causing negative sequence currents
Melting cage material of rotor is also an indication of thermal overloading.
Tests performed to find Rotor Problems:
Following tests are carried out to detect thermal effects upon rotors.
- Rotor influencer check
- Inrush/start up test
- Ultrasonic test
- Advanced Spectral Analysis
- No load saturation
- Motor monitoring during operation on test stand
Magnetic Stresses:
Dynamic forces are caused due to slot leakage flux which is proportional to the rotor current squared.
These forces can cause vibration of the rotor and can displace it radially. These types of magnetic forces also cause the rotor bars to bend and result in fatigue failure. Unbalancing of the magnetic field can cause the rotor to be pulled out and to hit the stator.
This will cause a severe damage to the machine. This probability of rotor to be pulled out is highest during starting of the motor. This condition is called Eccentricity.
Dynamic Stresses:
The rotor shafts observe tremendous amount of torque and should be designed to bear this value for a continuous operation. Excessive stress above the design limits will shorten the machine’s life. Out of limits centrifugal forces can cause the rotor to fly apart during operation.
Environmental Stresses:
These stresses are the poor ventilation, chemical attack, high humidity or anything in the environment that can attack the rotor and break down the rotor material.
Mechanical Stresses:
There are many causes that are classified as mechanical stresses. These stresses include casting defects, broken parts, loose lamination, incorrect fitting, incorrect air gap, bent shafts, bearing failure, misalignment and incorrect materials.
Residual Stresses:
These stresses are caused due to welding, casting, machining operations and brazing. These stresses are not damage the rotor and don’t not change geometry of the rotor.
How to determine the Motor & Rotor Faults?
It is a very much time taking and detailed process to locate the cause of the Motor’s and Rotor’s failure. Many things like condition of the rotor, application and history of the motor have to be taken into consideration for the determination of the failure cause.
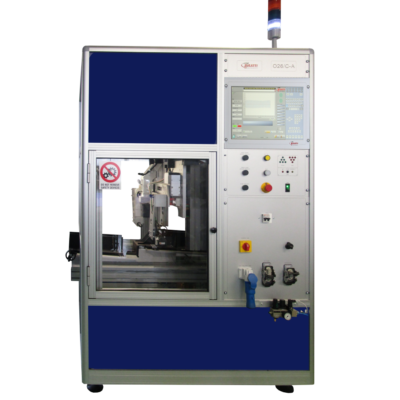
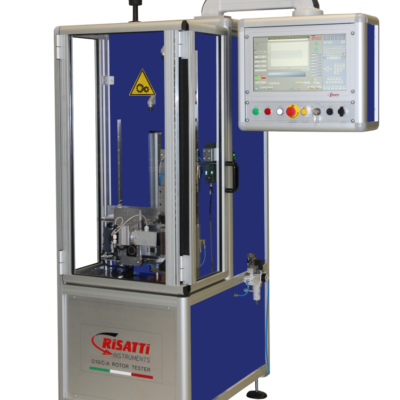
However, Risatti Instruments have made it easy to perform a lot of tests with “Z SERIES Computerized Automatic Systems” & “O SERIES DIE-CAST ROTOR TESTER “equipments.
Z SERIES Computerized Automatic Systems
These equipments are able to perform tests like ground efficiency, insulation resistance, dielectric strength, leakage current, functional tests and specific tests according to the testing object.
O SERIES DIE-CAST ROTOR BAR TESTER
This equipment is capable to find failure like interrupted bars, inclination of the bars, quality of aluminum alloy, blowing and porosities, blades leakage & cage eccentricity.
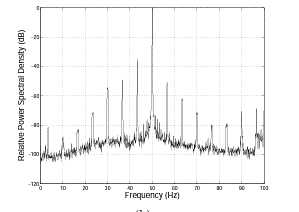

Many mechanical conditions, including rotor bar issues, cavitations, bearing faults, and others identified by current and torque spectra, are definable by using O series Testers.






